Women beware: Turns out you're three times more likely to suffer from the uncomfortable numbing, tingling and pain of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome than men.
Why? It's due to your smaller wrist bones which create a tighter space for all those pesky nerves and tendons in your forearm - especially between the ages of 45-54!
What causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, otherwise known as CTS, can cause a range of unpleasant symptoms including numbness and tingling in the hands. It's typically caused by pressure on the median nerve which connects from your forearm to your hand via an area called 'the carpal tunnel'.
Repetitive motions, genetics and even lifestyle factors can all lead to the compression of tendons in or around the carpal tunnel which leads to inflammation and pain.
Genetics play an especially important role for women as female carpal tunnels may be more narrow than average - while menopause and pregnancy-related hormonal changes also put pressure on nerves due its impact on swelling levels in this area.
The usual suspects such as smoking & obesity should never be underestimated either!
What are the symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
CTS is a condition that can start gradually, but if left untreated it can cause permanent damage. Symptoms typically include burning and tingling in the palm of your hand and fingers -- especially the thumb, index finger, and middle finger.
You may also feel pain shooting up your arm or weak/wasted muscles in your hands at night when trying to sleep - plus difficulty forming fists or grasping small objects during daytime activities.
Don't wait too long – timely diagnosis & treatment are essential for keeping Carpal Tunnel Syndrome under control.
How is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome treated?
Thankfully there are some simple treatments that might help reduce your discomfort: apply an ice pack to soothe any inflammation; aim for a good posture while working – especially if it involves repetitive motions or computer use - and take regular breaks; anti-inflammatory drugs may also provide relief.
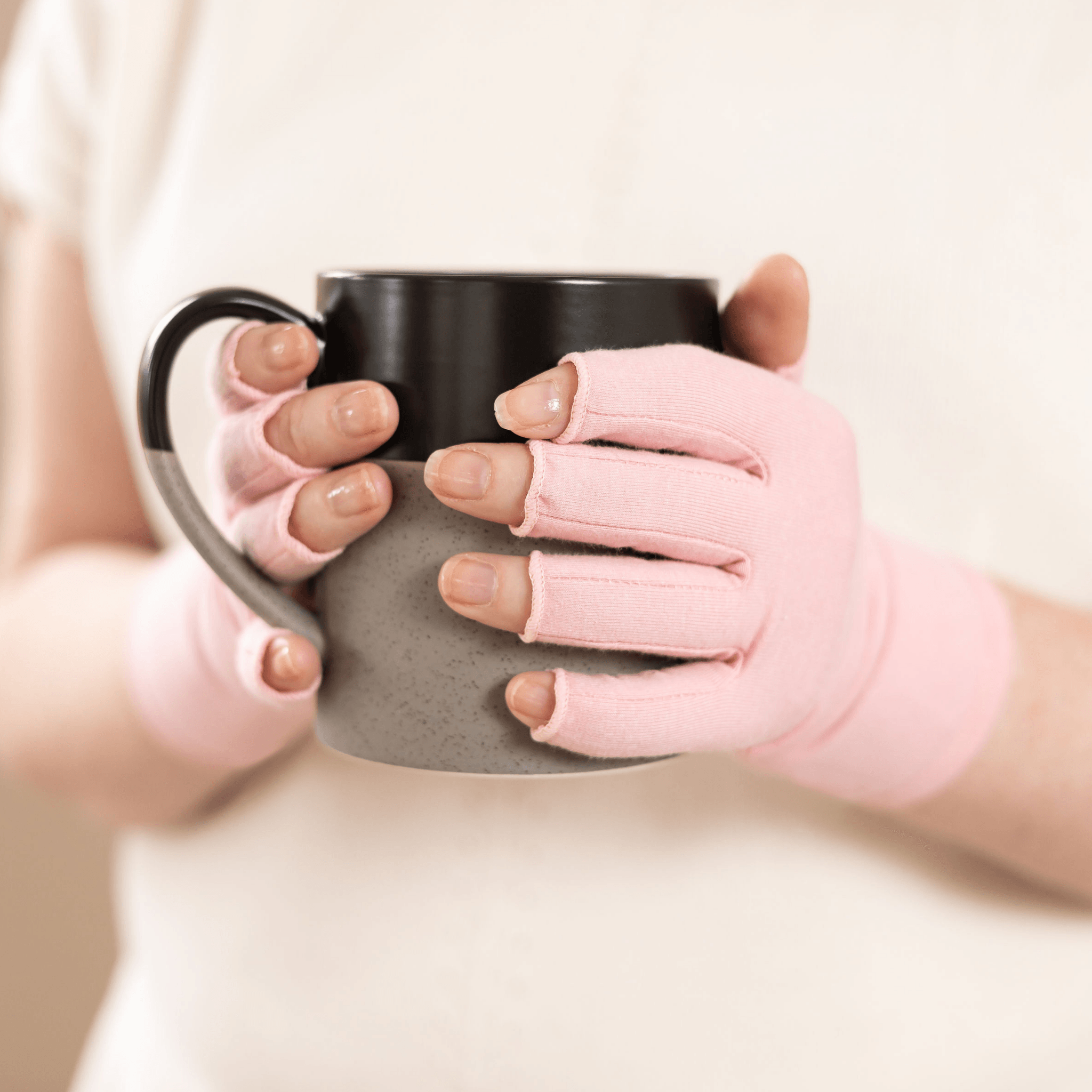
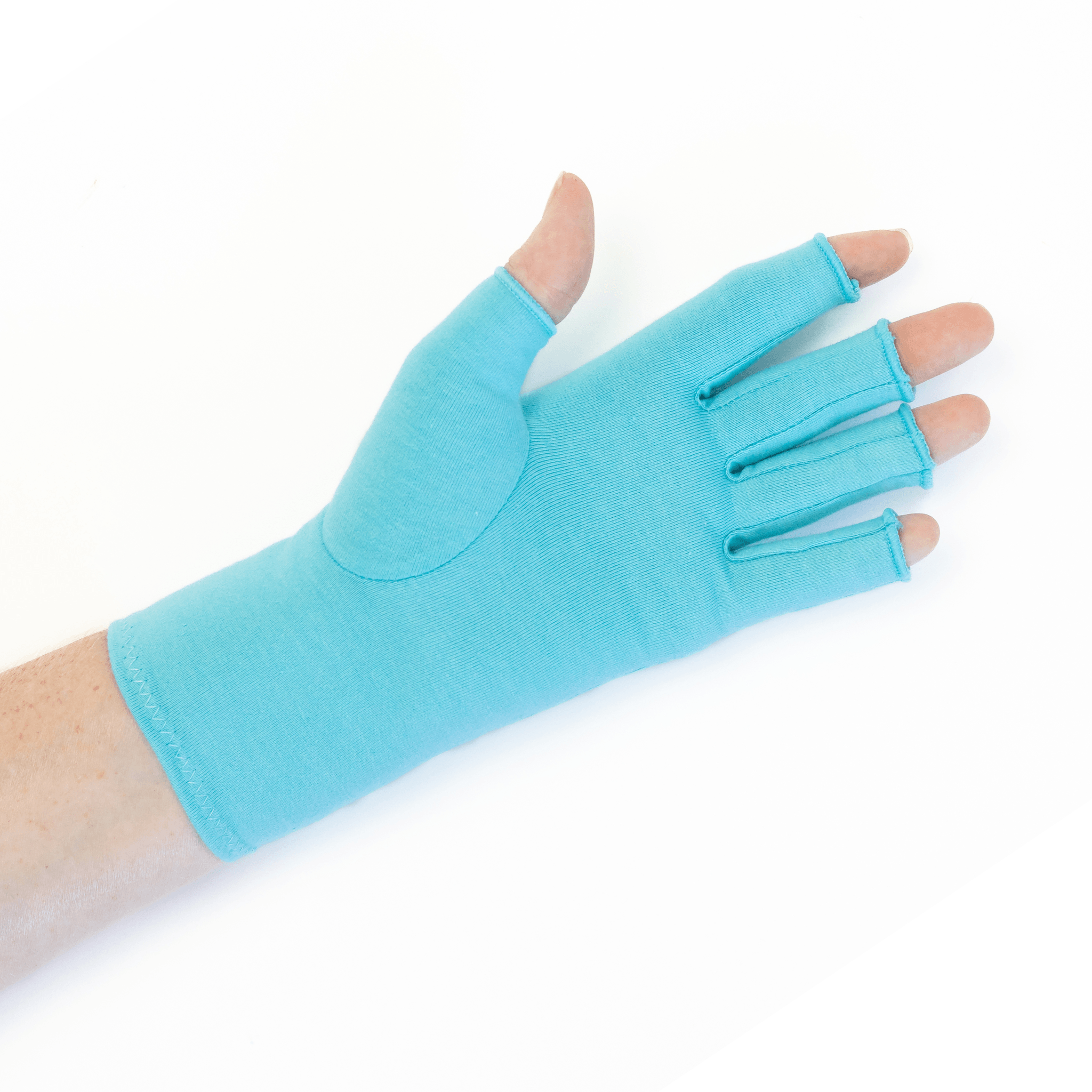
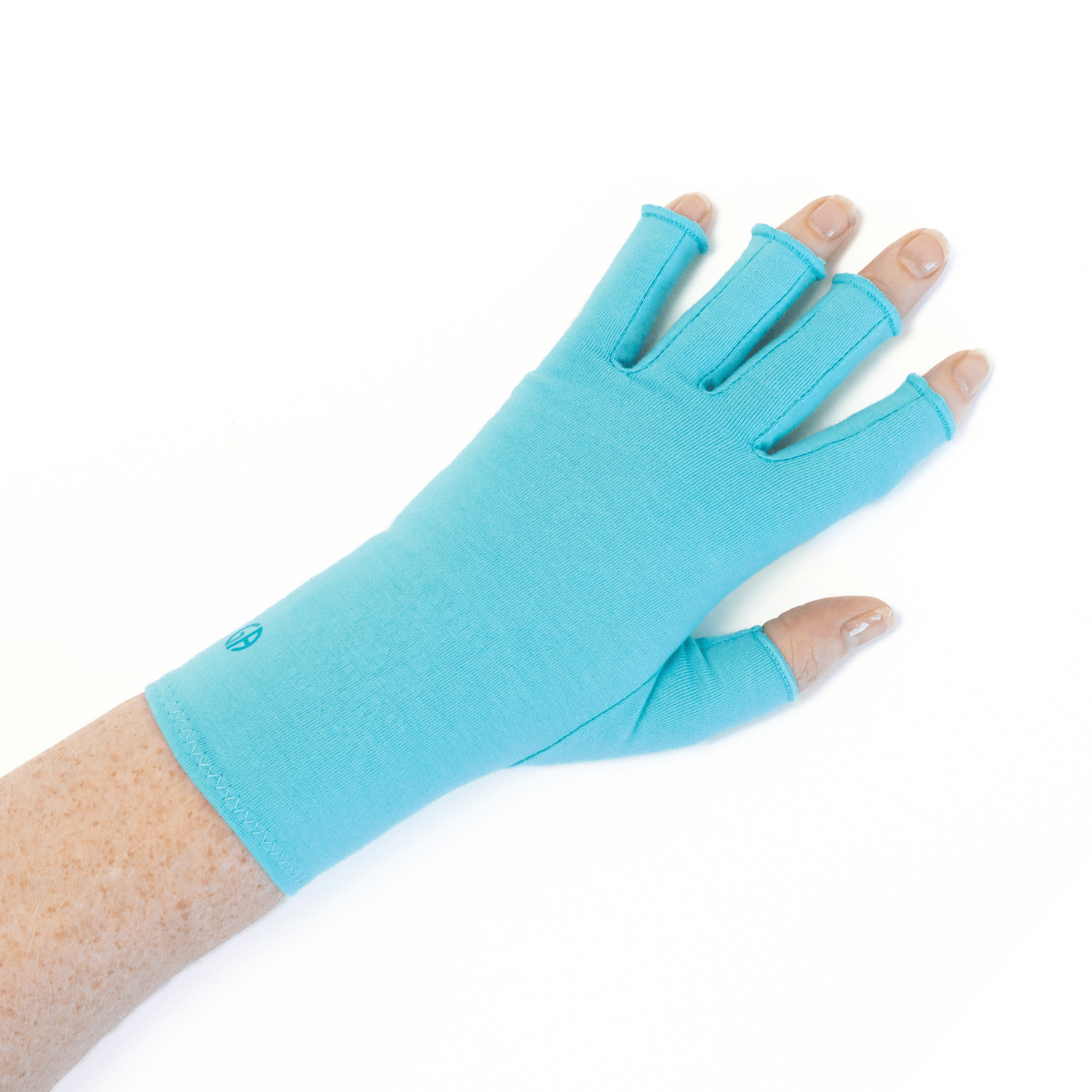
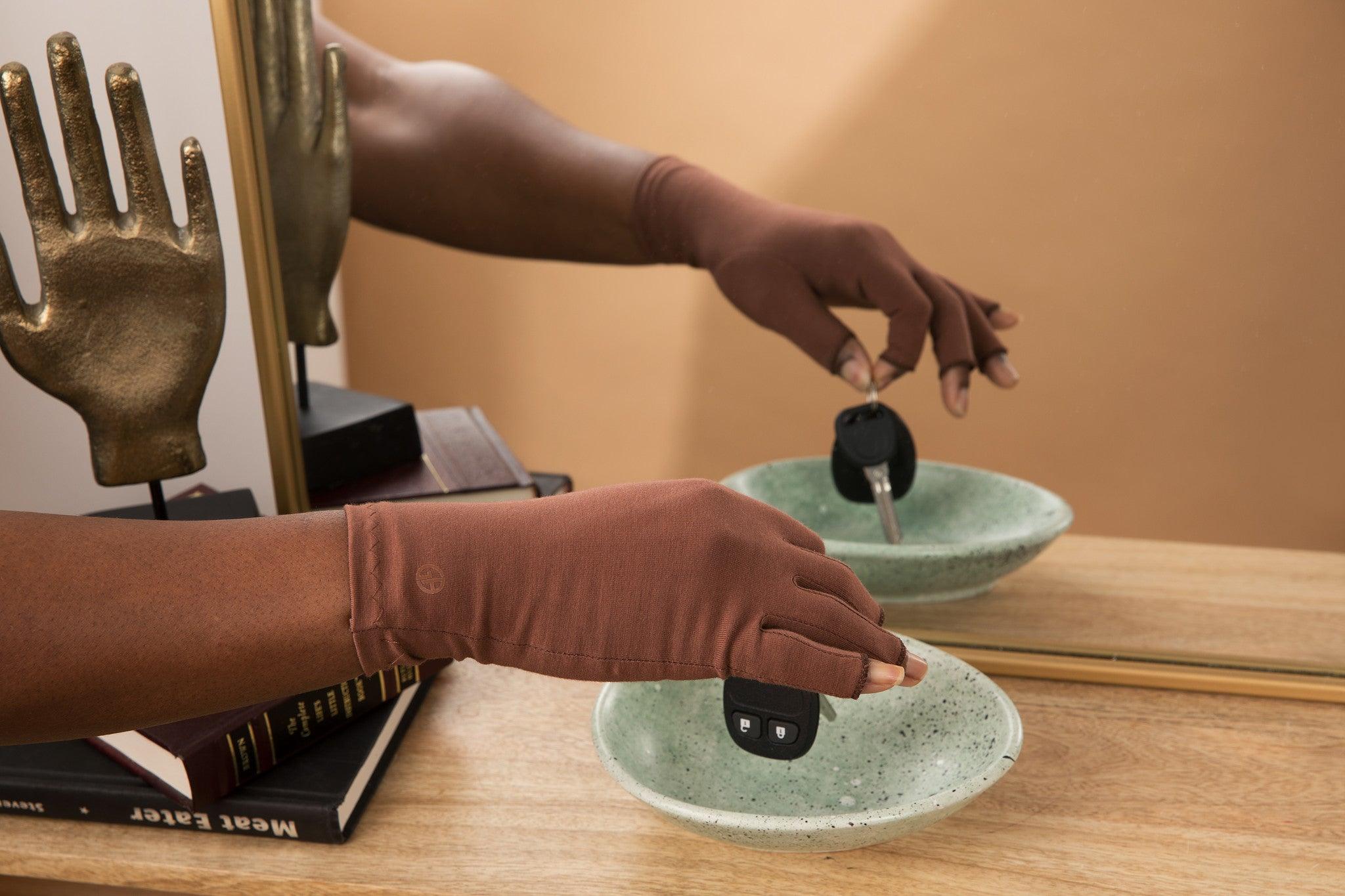
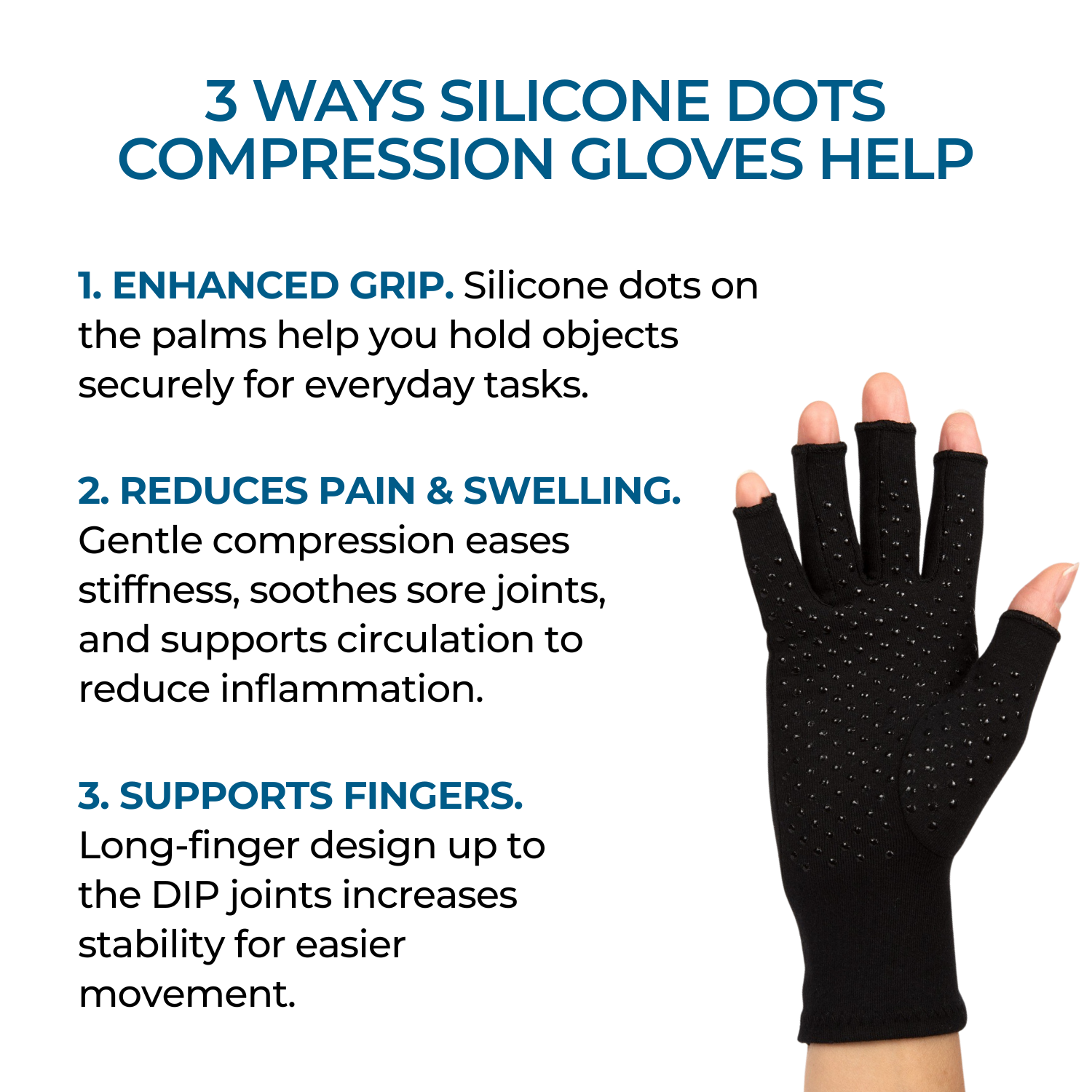
Wrist braces with splints will support your wrist in its neutral position to prevent further curling or balling movements that aggravate the condition. CTS Wrist Braces can be worn at night while you sleep.
If none of these approaches prove successful then surgery may be recommended by your medical practitioner. Always remember however, speak with a qualified doctor, hand surgeon or hand therapist before making any decisions when dealing with CTS symptoms





















































Share and get 15% off!
Simply share this product on one of the following social networks and you will unlock 15% off!